This is a comprehensive list of the over 270 construction tool names with pictures.
Table of Contents
ToggleWe have divided each construction tool into categories, so you can find exactly what you need.
They cover AR & VR, drones, surveying tools, and more. And this construction equipment list will give you complete knowledge of how each tool is used. So, check out the full list of construction tools and equipment and become a pro in your field.
Essential Building and Construction Tools Names with Pictures
Digital Tools for Construction work
Construction is a complex field that requires collaboration, coordination, and communication. To achieve the best results, construction professionals need digital tools to help them manage their workflow. In this section, we will explore some of the common digital construction tool names with images.
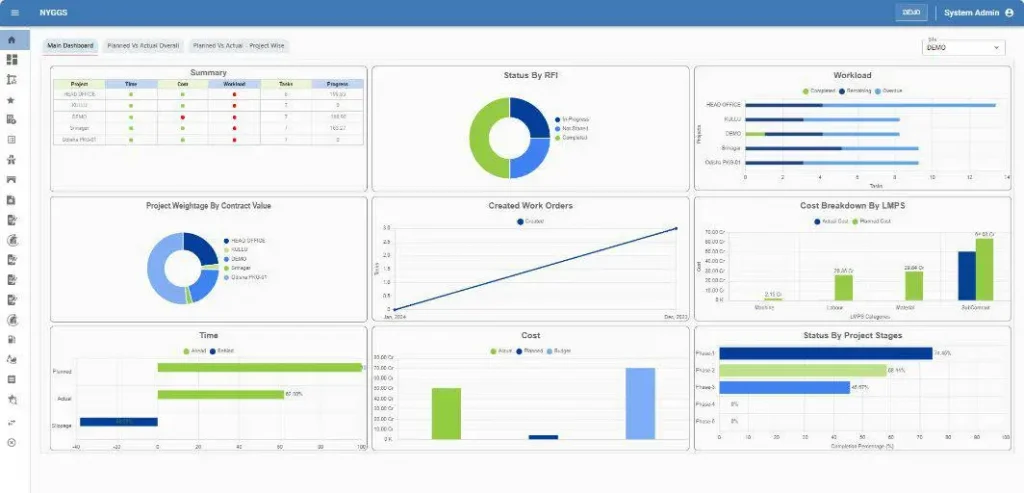
Construction Management Software (e.g., NYGGS Construction ERP)
Uses: A platform for planning, managing resources, budgeting, and real-time collaboration.
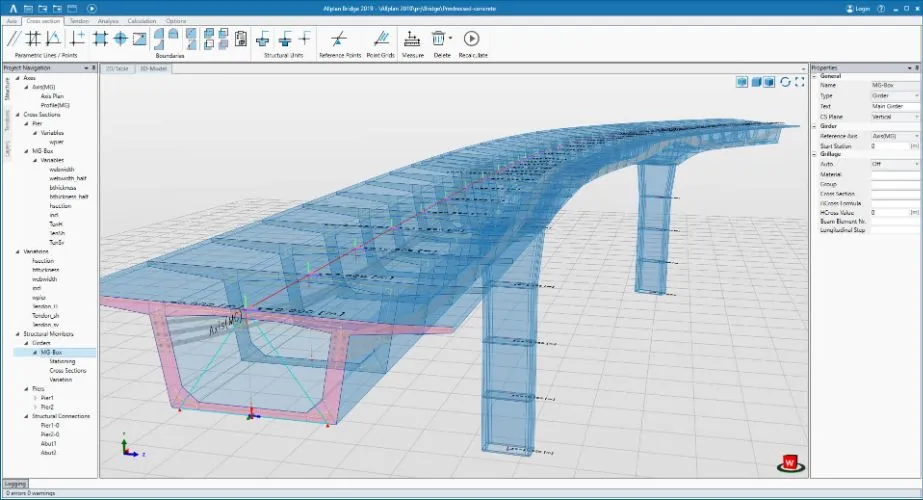
Building Information Modelling (BIM) Software
Uses: Use to create a digital model of a building’s physical and functional characteristics.
Uses: Used to share information digitally.
Uses: Captures aerial images and maps for surveying and monitoring.
Uses: Measures and scans existing structures and sites.

Construction Tools and Equipment for Lifting & Shifting of Materials
Lifting equipment refers to equipment used to lift loads, including slings, hooks, shackles, and other tools. Here, we list common construction tool names used for lifting and moving materials.
Uses: Lift and move heavy materials on construction sites.

Uses: Cranes for lifting and moving loads on-site.

Uses: Move and lift pallets in warehouses and on construction sites.

Uses: Lifting, carrying, and placing materials at different heights and distances.

Uses: Move materials and people between floors on construction sites.

Uses: Move materials horizontally or at an incline over short to medium distances.

Uses: Move pallets manually in warehouses and on flat surfaces at construction sites.

Uses: Move small loads of materials on construction sites.

Uses: Move heavy objects or stacks of materials over short distances.

Uses: Provide work platforms at different heights.

Uses: Reach high and far for work in hard-to-get-to places.

Uses: Lift and move heavy loads in a fixed area.

Uses: Dig and lift materials, like a digger with a crane.
Uses: Good for digging, grading, and moving materials in tight spaces.

Uses: Move construction materials up and down in multi-storey buildings.

Uses: A crane on a truck for lifting and moving.

Uses: A platform for working at heights in tight spaces.

Uses: A portable platform for working at different heights on construction sites.

Uses: A ladder for reaching high areas in construction and maintenance.

Uses: A pump for delivering concrete to precise locations on construction sites.

Construction Tool Names for Earthwork (Excavation, Backfilling & Compaction)
Earthwork is the process of moving part of the earth’s surface from one place to another by excavating, backfilling, or compacting. Below is a construction equipment list that includes tools used for this purpose.
Uses: Dig and move the earth. More mobile than crawler excavators.

Uses: Dig and move earth on tracks.

Uses: Good for digging, trenching, and light lifting on construction sites.

Uses: Move large amounts of soil, sand, rubble, and other materials in construction projects.

Uses: These machines can dig, load, and handle materials in tight spaces.

Uses: Dig narrow trenches for pipes, cables, or drainage.

Uses: Move materials like soil, gravel, and debris on building sites.

Uses: Transport and unload loose materials like sand, gravel, and demolition waste.

Uses: Compress soil, gravel, and asphalt to make them stronger.

Uses: Make surfaces even for building roads and preparing sites.

Uses: Vibrate soil to make it denser and more stable.

Uses: Drill deep foundations for large buildings.

Uses: Break up rock, concrete, or other hard materials.

Uses: Drill holes in the soil for posts, poles, or foundations.

Uses: Manual tools for digging, loosening soil, and moving small amounts of material.

Uses: Like a bulldozer but with tracks for difficult terrain.

Uses: Front-end loader for moving loose materials.

Dumper Truck
Uses: A smaller dump truck for building sites.

Uses: Compact soil, gravel, or asphalt in small spaces.

Uses: Compact soil in tight spaces.

Uses: Remove water from construction sites or excavations.

Uses: Flexible hose for water drainage.

Uses: Break concrete, rock, or pavement using air or water power.

Uses: Compact soil manually in small areas or trenches.

Uses: A long bar for breaking up hard soil or rock.

Uses: A tool for lifting heavy objects on construction sites.

Uses: A tool for digging, moving soil, or breaking up earth in small areas.

Construction Equipment List for Formwork
Formwork is the usually temporary structure used to contain and shape concrete to the required dimensions. To do this, contractors use the common formwork tools and equipment listed below.
Uses: Mould concrete into desired shapes for walls, columns, and other structural elements.

Uses: Hold formwork panels together and maintain proper spacing during concrete pouring.

Uses: Prevent concrete from sticking to formwork, allowing easy removal after curing.
Uses: Provide support and alignment for formwork panels, distributing pressure evenly.

Uses: Create round columns or piers by serving as moulds for poured concrete.

Uses: Secure formwork in place, particularly for ground-level concrete pours.

Uses: Drive nails, adjust formwork components, and perform various assembly tasks.

Uses: Quickly and efficiently fasten formwork components together.

Uses: Cut formwork panels and lumber to the required sizes and shapes.

Uses: Ensure accurate dimensions and placement of formwork components.

Uses: Mark straight lines on formwork for precise cutting and alignment.

Uses: Apply release agents evenly to formwork surfaces for easy concrete removal.

Uses: Shape and cut concrete, remove excess material, and create details.

Uses: Transport formwork materials, concrete, and tools around the construction site.

Uses: Serve as smooth, reusable formwork panels for high-quality concrete finishes.

Uses: Fasten formwork components together securely.

Uses: Adjust and secure formwork, allowing for easy dismantling.

Construction Tools and Equipment Required for Concrete Pouring Work
Concrete pouring is the process of placing, distributing, and consolidating the freshly mixed concrete in the desired location. The following are the common construction tool names required for this operation:
Concrete Pump Trucks
Uses: Deliver and pump concrete to hard-to-reach areas.

Uses: A mixer truck to mix concrete on-site.

Uses: Mix small amounts of concrete on-site for minor jobs.

Uses: Use this to transport and pour concrete in inaccessible areas.

Uses: Remove air bubbles from fresh concrete to make it stronger.

Uses: Guide concrete from trucks or buckets to specific locations.

Uses: Level and smooth concrete to achieve the right height.

Uses: Smooth and level larger concrete surfaces after initial screeding.

Uses: Spread concrete evenly before screeding and floating.

Uses: Manually move small amounts of concrete on-site.

Uses: Finish large concrete surfaces to a polished look.

Uses: Precisely place concrete in various locations from a single pump truck.

Uses: Transport larger amounts of concrete across construction sites than wheelbarrows.

Uses: Flexible conduits to deliver pumped concrete to specific pouring locations.

Uses: Store and control the release of concrete from trucks or mixers.

Uses: Produce large volumes of concrete on-site, ensuring consistent quality and supply.

Construction Equipment & Machinery for Concrete Finishing Work
Special tools and equipment are necessary for carrying out concrete finishing after compaction. Below are some common construction tool names used in this process.
Uses: Smooth large concrete surfaces quickly for a flat, polished finish.

Uses: Finish smaller concrete areas or edges by hand.

Uses: Make concrete slabs look finished and safe with rounded edges.

Uses: Cut decorative lines or control joints in fresh concrete.

Uses: Make concrete surfaces smooth and level.

Uses: Add patterns or textures to fresh concrete for decoration.

Uses: Cut shapes in hard concrete.

Uses: Smooth or remove coatings from rough concrete.

Uses: Make concrete floors shine.

Uses: Use curing agents on fresh concrete to help it set.

Uses: Make concrete surfaces non-slip.

Uses: Make fresh concrete surfaces have the same texture.

Uses: Cut hardened concrete for repairs, demolition, or modifications.

Uses: Apply coatings to concrete surfaces.

Uses: Remove air bubbles from freshly poured concrete.

Uses: Clean concrete surfaces before finishing.

Uses: Smooth and level larger areas of freshly poured concrete.

Uses: Remove high spots on hardened concrete.

Construction Tool Names Required for Plastering
Plastering is an age-old technique that involves applying a thin layer of plaster, a mixture of lime or cement, sand, and water, to the exposed surface of walls, ceilings, or partitions. Workers use some specialised construction tools and equipment, which are listed below.
Uses: Apply and smooth plaster on walls and ceilings.

Uses: Hold plaster while working, allowing easy access for the trowel.

Uses: Smooth and level plaster surfaces after initial application.

Uses: Blend plaster materials to achieve proper consistency for application.

Uses: Efficiently deliver mixed plaster to application areas, especially for large projects.

Uses: Provide elevated work platforms for plastering walls and ceilings.

Uses: Remove excess or old plaster and prepare surfaces for new applications.

Uses: Create clean, sharp corners and edges on plastered surfaces.

Uses: Ensure straight and level plaster application, especially for large areas.

Uses: Level and smooth large areas of wet plaster.

Uses: Hold and transport mixed plaster for easy access during work.

Uses: Achieve specific textures and finishes on plastered surfaces.

Uses: Ensure vertical alignment of plastered surfaces and corners.

Uses: Apply plaster quickly and evenly over large areas.

Uses: Smooth dried plaster surfaces and prepare them for painting or finishing.

Specialised Construction Tools and Equipment Required for Demolition Work
Demolition is the process of safely dismantling, destroying, or tearing down buildings and other man-made structures. It is a process that requires careful execution and specialised tools. Below, we have listed some construction tool names used in demolition.
Uses: Break and remove large structures with powerful arms.

Uses: Demolish buildings with heavy metal balls.

Uses: Machines controlled from a distance for precise demolition in dangerous or small spaces.

Uses: Break concrete, asphalt, or rock with a hammer.

Uses: Pulverise concrete and separate rebar for recycling.

Uses: Break walls, floors, or other structures manually.

Uses: Cut through concrete, metal, or other materials during demolition.

Uses: Use to separate materials, remove nails, or pry apart building components.

Uses: Cut through different materials in tight spaces during demolition.

Uses: Break concrete or rock with air hammers.

Uses: Split concrete or rock using hydraulic pressure.

Uses: Cut through metal during demolition.

Uses: Cut through metal with high-temperature flames.

Uses: These machines are good for small demolition and debris removal.

Uses: Control dust during demolition to improve safety and visibility.

Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Required in Construction
When it comes to the safety of construction workers, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a must. Below is a list of some of the most common PPE.
Uses: Protect your head on construction sites.

Uses: Protect your eyes from debris, dust, and the sun during construction work.

Uses: Protect your ears from loud noise on construction sites.

Uses: Filter out dust, fumes, and particles in construction.

Uses: Protect feet from falling objects and make them slip-resistant on construction sites.

Uses: It helps workers be seen in low-light or busy areas.

Uses: Protect hands from hazards during construction tasks.

Uses: Prevent falls from height when working on ladders or platforms.

Uses: Protect the whole face from debris, sparks, and chemical splashes.

Uses: Protect your whole body from dirt and chemicals on construction sites.

Uses: Protect your knees when you’re kneeling or crawling on hard surfaces.

Uses: Connect harnesses to anchor points to prevent falls.

Uses: Protect your eyes and face from welding light and sparks.

Uses: Protects skin from harmful chemicals used in construction.

Uses: Wear armour to protect your arms from cuts and abrasions when handling sharp materials or tools.

Post-Tensioning, Pre-Stressing & Grouting Work Construction Tool Names
Post-tensioning is important to ensure that the concrete is strong enough. Meanwhile, grouting is the process of using a mixture to repair cracks, fill gaps, seal joints and stabilise the ground. Discover the construction tools and equipment used for both purposes.
Uses: Use to tension cables or tendons in concrete structures.

Uses: Put prestressing strands into concrete ducts.

Uses: Use hydraulic pressure to tension cables or tendons.

Uses: Apply tension to cables in post-tensioning.

Uses: Inject grout into tendon ducts to protect the strands.

Uses: Cut excess strands after stressing.

Uses: Keep the prestressing strands in the ducts at the right distance and in the right position.

Uses: Keep tendons in place during concrete work.

Uses: Secure strands at the ends of concrete.

Grout Mixers
Uses: Mix cement-based grout for injection into tendon ducts.

Uses: Monitor hydraulic pressure during tensioning and grouting.

Uses: Check that strands elongate correctly during tensioning.

Uses: Group and organise strands for easier installation and tensioning.

Uses: Connect tendon ducts to ensure continuous paths for strands.
Uses: Measure and control grout injection rates during grouting.

Pavement Building Construction Tool Names with Pictures
Check out the essential building construction tool names with pictures used for pavement.
Uses: Lay down and compact hot asphalt for roads and parking lot surfaces.

Uses: Use concrete pavers to build rigid pavements for roads and airports.

Uses: Form and place concrete pavement without forms.

Uses: Compact the surface to achieve a smooth finish.

Uses: Remove old asphalt for recycling or to make way for new layers.

Uses: Use liquid asphalt to bond pavement layers.
Uses: Cut control joints in concrete to stop it from cracking.

Uses: Make concrete pavements skid-resistant by texturing them.

Uses: Use curing compounds on fresh concrete to help it harden.

Uses: Make hot mix asphalt by mixing aggregates, binder, and filler.

Uses: Move hot asphalt from trucks to pavers.

Uses: Spread stone or gravel for road construction.

Uses: Mark finished road surfaces with paint or thermoplastic.

Uses: Put steel bars in concrete pavements to carry loads across joints.

Building Construction Tool Names with Pictures Required for Operation & Maintenance Work
It covers the activities you put in place to keep your business running, including the maintenance of electrical, plumbing, HVAC, and security systems. Here we give you a construction equipment list of the tools used for this operation and maintenance work.
Uses: Measure electrical properties like voltage, current, and resistance in various circuits and equipment.

Uses: Quickly check for the presence of electrical current in wires or outlets.

Uses: Grip and turn pipes and fittings in plumbing and mechanical systems.

Uses: Tighten or loosen nuts and bolts of various sizes.

Uses: Fasten or remove screws in different types of equipment and fixtures.

Uses: Grip, bend, and cut wires or small components in electrical and mechanical work.

Uses: Remove insulation from electrical wires for connections or repairs.

Uses: Drive nails, break small objects, or provide force in various maintenance tasks.

Uses: Create holes or drive screws in various materials for installations or repairs.

Uses: Visually examine hard-to-reach areas in equipment, pipes, or structures.

Uses: Detect heat patterns to identify electrical or mechanical issues non-invasively.

Uses: Apply lubricants to moving parts in machinery to reduce friction and wear.

Uses: Clean exterior surfaces, equipment, or vehicles using high-pressure water spray.

Uses: Power pneumatic tools and clean equipment using compressed air.

Construction Equipment & Machinery Required for Repairing Work
In construction, repair means fixing problems in buildings, equipment, or machinery. See the list of common construction tool names used for repairs.
Uses: Join metal parts by melting them together.

Uses: Join metal parts with solder, usually for electrical or plumbing work.

Uses: Cut, grind, and polish metal or masonry.

Uses: Cut through materials in tight spaces or for demolition work.

Uses: Drive nails into wood or other materials for fast assembly.

Uses: Cut curves and shapes in wood, plastic, or thin metal.

Uses: Use sealants or adhesives to waterproof or bond.

Uses: Use to apply and smooth putty, spackle, or other fillers in surface repairs.

Uses: Use to remove nails, separate materials, or pry apart components.

Uses: Cut wood, stone, or metal for repairs.

Uses: Shape metal, wood, or plastic.

Uses: Tighten nuts and bolts to the right torque for assembly.

Uses: Tighten screws and bolts with high torque.

Uses: Use heat to remove paint, thaw pipes, or soften adhesives.

Essential Resources Required for Construction Site Setup Work
Building a structure starts with setting up the site. Here are some common tools and equipment for this initial construction phase.
Uses: Keep construction sites safe and secure.

Uses: Provide clean toilets for workers on-site.

Uses: They can be used as offices and meeting spaces.

Uses: Store tools, equipment, and materials safely on-site.

Uses: Power tools, equipment, and temporary structures on construction sites.

Uses: Light up work areas in the dark for safety and productivity.

Uses: Store and supply water for construction and for workers.
Uses: Tell workers and visitors about safety issues.

Uses: Provide medical help and supplies for injuries or emergencies.
Uses: Collect and manage construction waste.
Uses: Clean workers and equipment before leaving contaminated areas.

Uses: Make surfaces stable for vehicles and equipment on soft or uneven ground.
Uses: Keep the construction site safe from theft.

Uses: Monitor the weather to make sure it is safe to work and plan activities.

Tools and Equipment Required for Power Supply to Construction Site
Have a look at this list of construction tool names used for uninterrupted power supply to the construction site.
Uses: Provide primary or backup electrical power for construction equipment, lighting, and temporary facilities.

Uses: Safely distribute electricity from generators to multiple tools and equipment.

Uses: Deliver power to tools and equipment across the construction site.

Uses: Adjust voltage levels to match the power requirements of different equipment and tools.

Uses: Control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment in the power distribution system.

Uses: Automatically interrupt electrical flow in case of overload or short circuit.

Uses: Distribute power and house circuit breakers for different areas or equipment.

Uses: Support and organise electrical cables and wiring across the construction site.

Uses: Protect and route electrical wiring throughout the construction site.

Uses: Maintain consistent voltage levels for sensitive equipment and tools.

Uses: Monitor and measure electrical consumption for cost tracking and load management.

Uses: Store fuel for generators to ensure continuous power supply.

Uses: Store electrical energy for use during peak demand or as backup power.
Uses: Generate renewable energy for small power needs or to supplement the main power supply.

Uses: Provide instantaneous backup power to critical equipment during main power interruptions.
Essential Tools and Equipment for Night Shift Work at the Construction Site
Construction projects often require night shifts to meet deadlines, avoid traffic, or reduce noise and environmental impacts. Workers use special tools and equipment to work safely at night.
Uses: Illuminate large areas of the construction site at night.

Uses: Light specific work areas with bright, directed light.

Uses: Let workers see what they’re doing in dark or small spaces.

Uses: Make workers more visible at night.

Uses: Use personal protection and illumination to make workers more visible and safe.

Uses: Use to mark hazards or emergencies.

Uses: Make equipment, barriers, and hazards more visible in low light.

Uses: Monitor security and work progress in low light.
Uses: Bright, energy-efficient lighting for specific areas or equipment.

Uses: Provide reliable lighting that doesn’t depend on the main power supply.

Uses: Provide soft, glare-free illumination over large areas.

Uses: Integrate lighting into construction equipment for safer operation at night.
Uses: Clearly display information, directions, and warnings during night shifts.
Uses: Spread light to reduce glare and create more even illumination.
Uses: Provide intense, focused lighting for detailed work or inspections at night.

Construction Equipment List for Dewatering at the Construction Site
Dewatering is the removal of groundwater or surface water from a construction site. It is important for stabilising the ground. The process requires special construction tools and equipment. Below are some of the construction tool names used for the dewatering process.
Uses: Pump water out of excavations underwater.

Uses: Use small wells and vacuum pumps to lower groundwater levels.

Uses: Filtered water is discharged after trapping sediment.

Uses: Remove water from basements, crawl spaces, or pits.

Uses: Remove large volumes of water and sediment from construction sites.

Uses: Remove suspended solids from water before discharging or treating it.

Uses: Separate solids from liquids in dewatering sludge to reduce waste.

Uses: Move large amounts of water quickly. Ideal for surface water removal.

Uses: Move water from where it is pumped to where it is treated.

Uses: Monitor water levels during dewatering.

Uses: Measure and record the water pumped during dewatering.

Uses: Stop debris from damaging pumps when removing water.

Uses: Send pumped water to different places for disposal or treatment.

Uses: Power pumps in areas without reliable electricity.

Uses: Make sure the water is clean before you release it.
Construction Tools, Equipment & Machinery Required for Surveying Work
Construction surveying is used to locate and align man-made objects like highways, bridges, and buildings. The main construction tool names with pictures for surveying used around the world are:
Uses: Measure angles and distances to determine the precise positions of points on construction sites.

Uses: Determine accurate geographical coordinates using satellite signals for site mapping and layout.

Uses: Project level lines across construction sites for accurate grading and elevation measurements.

Uses: Measure horizontal and vertical angles for precise positioning and alignment in construction.

Uses: Quickly measure linear distances on construction sites for rough estimates and layouts.

Uses: Measure vertical distances and serve as targets for other surveying instruments.

Uses: Provide stable platforms for mounting and operating various surveying instruments.

Uses: Measure distances to objects or points without physical contact, useful for inaccessible areas.

Uses: Measure angles of slope or elevation in terrain or structures.

Uses: Return signals to total stations for accurate distance and position measurements.

Uses: Capture aerial imagery and data for site mapping and progress monitoring.

Uses: Process, analyse, and visualise surveying data to create maps and site plans.
Essential Tools and Equipment Required for Traffic Management at the Construction Site
Good traffic management can help minimise the movement of vehicles and paddlers around a site and maximise site safety. Below are some tools and equipment used to manage traffic on and around a construction site.
Uses: Control traffic in work zones with temporary traffic lights.

Uses: Guide drivers to change lanes or merge in construction areas.

Uses: Show road conditions, detours, and construction information.

Uses: Mark construction areas and guide traffic.

Uses: Block off and redirect traffic away from construction zones.

Uses: Mark temporary traffic patterns in work zones.

Uses: Install temporary road signs for construction information and directions.

Uses: Measure vehicle volume through work zones.

Uses: Monitor vehicle speeds in construction areas to enforce speed limits.
Uses: Warn drivers of upcoming work zones.

Uses: Change traffic signals to suit new traffic patterns around construction.

Uses: Let workers know when vehicles enter restricted areas.
Uses: Absorb impact in case of collision.

Uses: Keep traffic and workers separate in work zones.

Uses: Guide pedestrians safely through construction areas.
Anything We Missed on Construction Tool Names?
Those are the most common construction tools and equipment used across the world.
And now we’d like to hear from you:
Are there any tools or equipment that you know… but didn’t see on this list?
Or maybe you have a question.
Either way, let us know by contacting us right now.
Disclaimer:
Image Usage
The images used in this blog post are for illustrative and educational purposes only. They do not represent an endorsement or promotion of any specific brand or product.
Copyright
We respect the copyright of all image owners. Every effort has been made to credit the original sources of the images used in this blog post. If you believe that any image has been used without proper attribution or in violation of copyright law, please contact us immediately, and we will take appropriate action.
And the information provided in this blog post is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice.







